The cover image for this post is by Mariia Shalabaieva
Introduction
Phishing emails are becoming increasingly sophisticated, making it harder for individuals to distinguish between legitimate and scam emails. With the rise of social engineering tactics, scammers can create emails that appear to be from trusted companies or institutions, such as Microsoft, in an effort to trick victims into divulging sensitive information or clicking on malicious links. In this blog post, we’ll explore the common signs of phishing emails, including red flags that your email provider might flag, suspicious email addresses, poor design language, and more.
We’ll use a real email that a family member received, with the promise that they will remain anonymous. All of the commentary and screenshots in this blog post are from this, very real, email.
The Anatomy of a Phishing Email
When a phishing email arrives in your inbox, take a closer look at the sender’s email address. Legitimate companies like Microsoft always use their official domain (e.g., @microsoft.com) for emails sent from legitimate accounts.
In our example, the scammers used “microsoftmicrosoft584@gmail.com,” which is unlikely to be an authentic Microsoft email. Scammers often create fake email addresses that mimic those of reputable companies by modifying only a few characters or using variations of the company’s name.

.
For example, instead of using “awards@microsoft.com,” (which is a made up email address, for this blog post) they used “microsoftmicrosoft584@gmail.com.” This attempt to create a fake email address that appears similar to Microsoft’s official domain is a common tactic used by scammers. Legitimate companies will never use such modified domains for their official communications.
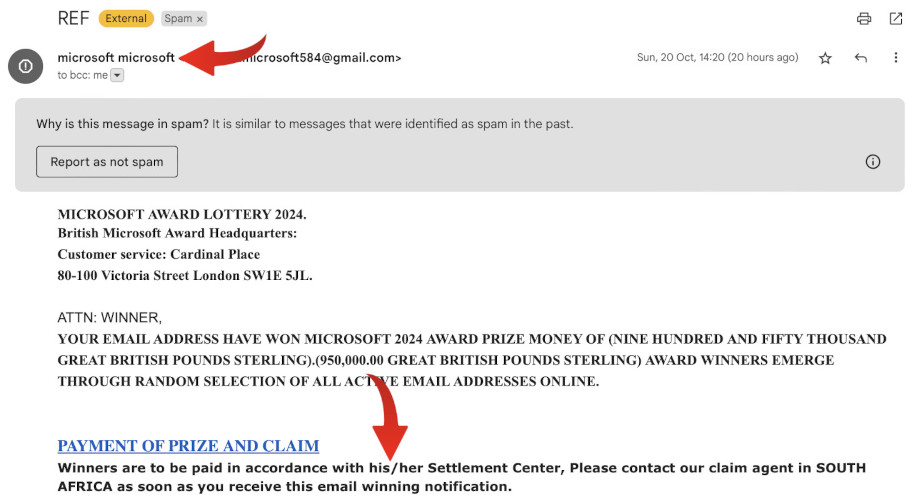
Display Name and Pronouns
Legitimate companies usually use professional display names that match their public branding. The scammers in our example used a display name with all lowercase letters, which is unusual for any reputable company. In contrast, Microsoft or its employees would typically use a display name like “Microsoft Award Lottery Team” or similar.
.
Moreover, legitimate companies will use pronouns that are specific to an individual recipient. The scammers in our example mentioned vague pronouns (his/her) which potentially do not match the pronouns of the email recipient. This is another red flag indicating that the email might not be from a trusted source.
Use of BCC and ALL CAPS
Phishing emails often use blind carbon copying (bcc) to send the same email to multiple recipients without revealing their addresses. Legitimate companies typically address you directly in the “To” field, rather than using bcc. Scammers may use bcc to avoid detection by spam filters or email providers.

.
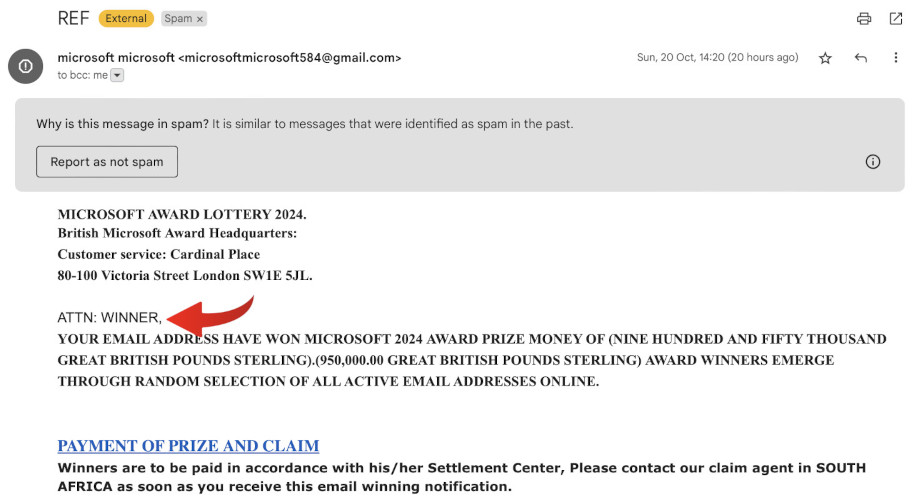
Another red flag is the excessive use of ALL CAPS in the email body. While some legitimate emails may use bold text or emphasize certain words, almost no reputable company uses ALL CAPS for entire sentences. This type of formatting can come across as unprofessional and may indicate that the email is not from a trusted source.
.
Design Language and Legitimacy
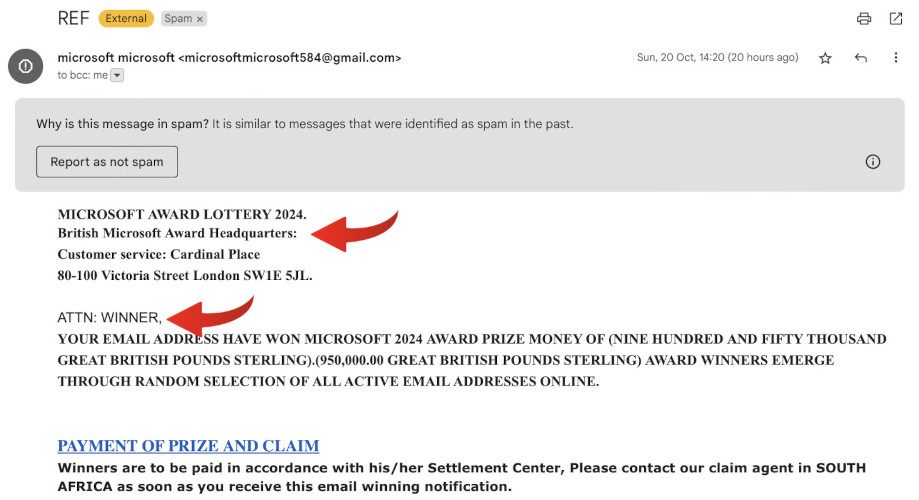
Legitimate companies have a consistent design language for their emails, which matches their public branding. Our example email lacked this consistency, using plain text and an unprofessional font (in this case Times New Roman) that doesn’t align with Microsoft’s design language (which uses Segoe UI).
.
A legitimate company will always strive to maintain a consistent visual identity in their emails, which includes typography, color schemes, and layout. This consistency is essential for building trust with customers and establishing credibility. In contrast, phishing emails often use tactics like using different fonts or colors to create a sense of urgency or fear.
Red Flags Your Email Provider Might Raise
Many email providers flag suspicious emails as “spam” due to their suspicious characteristics. Our example email was flagged by our provider due to its similarity to past spam messages. These flags can be an important indicator that the email may not be from a trusted source.
.
When your email provider flags an email as “spam,” it means that they’ve identified certain characteristics in the email that suggest it might be malicious or unsolicited. These flags can help you avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from suspicious emails.
Conclusion
Phishing emails are becoming increasingly sophisticated, but there are common signs that can help you spot them. Pay attention to suspicious sender addresses, poor design language, and inconsistencies in the email content. Remember, legitimate companies will always use their official domain, address you directly, and maintain a consistent design language.
By being aware of these red flags, you can protect yourself from phishing scams and keep your personal data safe.
Additional Tips
- Be cautious of emails that promise unusually large prizes or offer rewards for participating in a “lottery.” Legitimate companies will never ask you to participate in such schemes via email.
- Legitimate companies will never ask you to provide sensitive information, such as passwords or financial details, via email. If an email requests this type of information, it’s likely a phishing attempt.
- Always verify the authenticity of an email by contacting the company directly using their official contact information. This can help you determine if the email is legitimate and not from a scammer.
- The old adage of “if it seems to good to be true, it probably isn’t,” always fits with everything Internet-based.
Stay safe online, and stay vigilant against phishing scams!
Learn more about how you can leverage our bespoke software development and podcast editing and mastering services today.
If you’d like us to help you work through the challenges involved with your software development or podcasting projects, either in a hands-on capacity or as a consultant, get in touch with the form below
